Disorders of brain overgrowth can cause intractable epilepsy, intellectual disability, and autism. They are caused by mutations that activate the RTK-PI3K-AKT signalling cascade in the brain, which regulates the mTOR pathway. At ENCORE we focus in particular on M-CAP Syndrome (Megalencephaly capillary malformation syndrome) which is caused by mutations in the PIK3CA gene, MPPH Syndrome (Megalencephaly, polymicrogyria, polydactyly syndrome) which is caused by mutations in the AKT3 gene, CCND2 gene or the PIK3R2 gene, Smith-Kingsmore syndrome which is caused by mutations in the mTOR gene, and Megalencephaly is caused by mutations in the STRADA/LYK5, PP2A subunits (PPP2R5B, PPP2R5C, PPP2R5D) and RHEB.
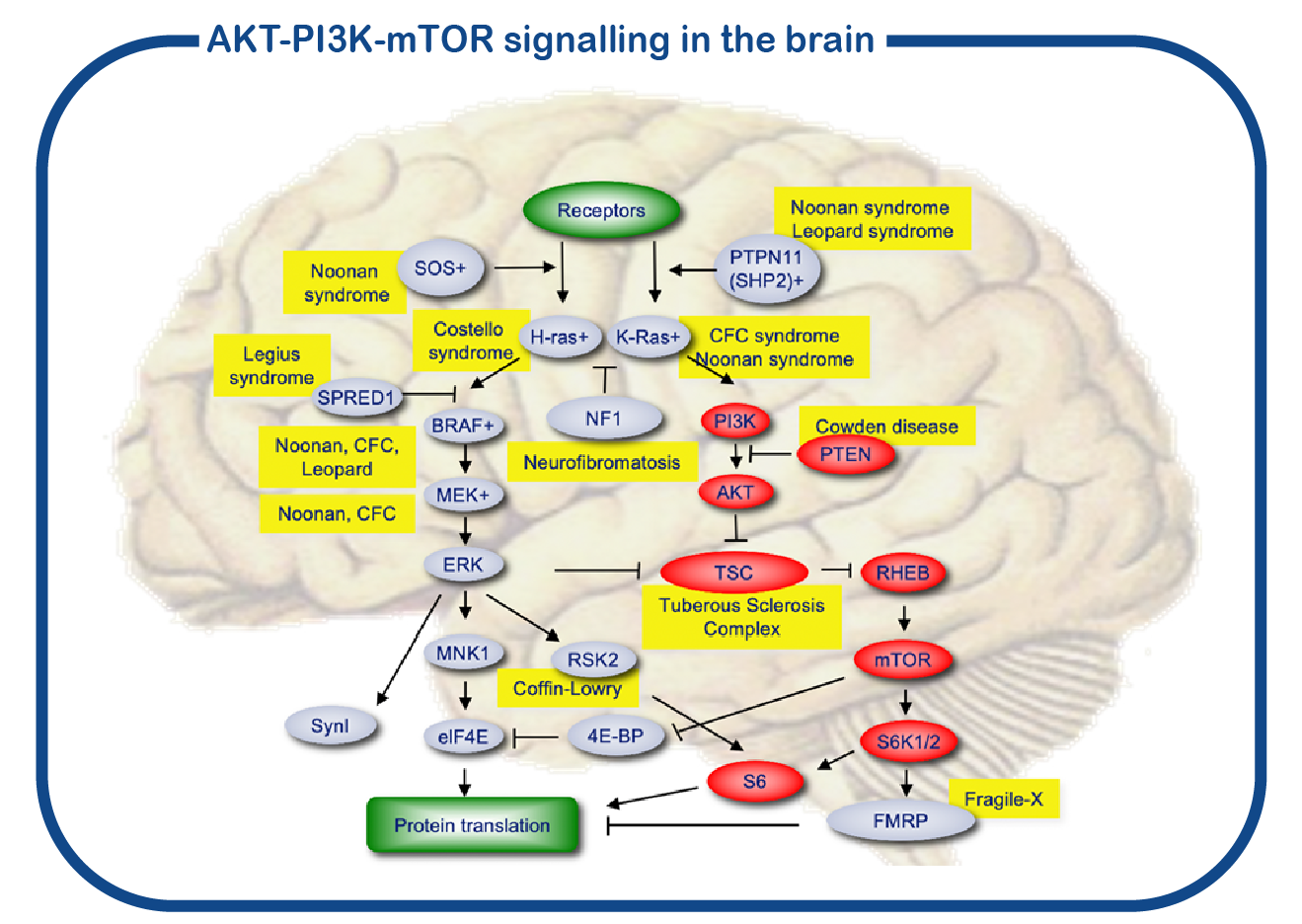
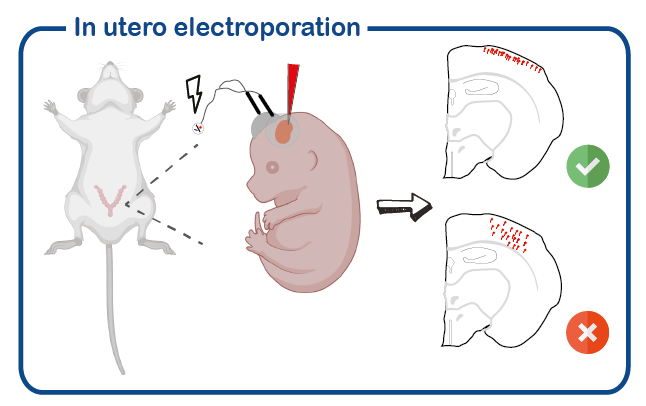
Brain overgrowth research at ENCORE is primarily focusing on the role of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR signalling in the brain. For that we use both mouse models (TSC, RHEB) as well as in utero electroporation of mice.
Mancini GMS, et.al. (2021) Multidisciplinary interaction and MCD gene discovery. The perspective of the clinical geneticist. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 35:27-34 Pubmed
Douzgou S, et.al. (2021) A standard of care for individuals with PIK3CA-related disorders: An international expert consensus statement. Clin Genet. Pubmed
Besterman AD, et.al. (2021) Functional and structural analyses of novel Smith-Kingsmore Syndrome-Associated MTOR variants reveal potential new mechanisms and predictors of pathogenicity. PLoS Genet. 17(7):e1009651. Pubmed
Proietti Onori M, et.al. (2021) RHEB/mTOR hyperactivity causes cortical malformations and epileptic seizures through increased axonal connectivity. PLoS Biol. 19(5):e3001279. Pubmed
Reijnders M, et.al. (2017) Variation in a range of mTOR related genes associated with intracranial volume and intellectual disability. Nat Commun. 8(1); 1052. Pubmed
