Monozygote (‘identieke’) tweelingstudies hebben aangetoond dat autisme in hoge mate erfelijk is. In het afgelopen decennium zijn er veel genen geïdentificeerd die, wanneer ze gemuteerd zijn, autisme kunnen veroorzaken. Een uitgebreide lijst van deze ‘autisme’-genen wordt hieronder weergegeven (bron: www.SFARI.org; bijgewerkt in januari 2020).
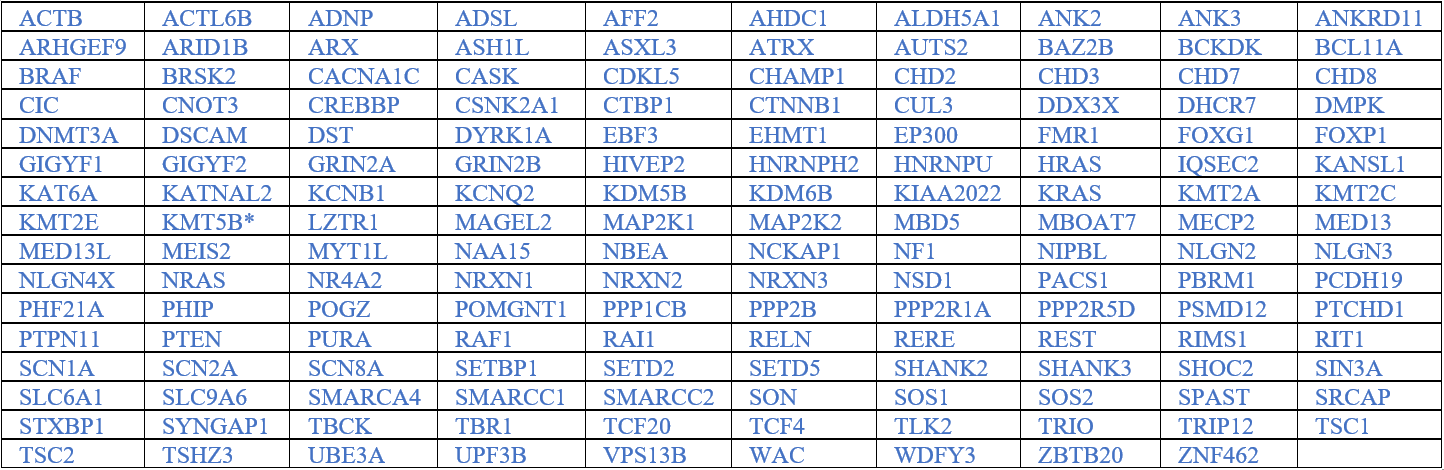
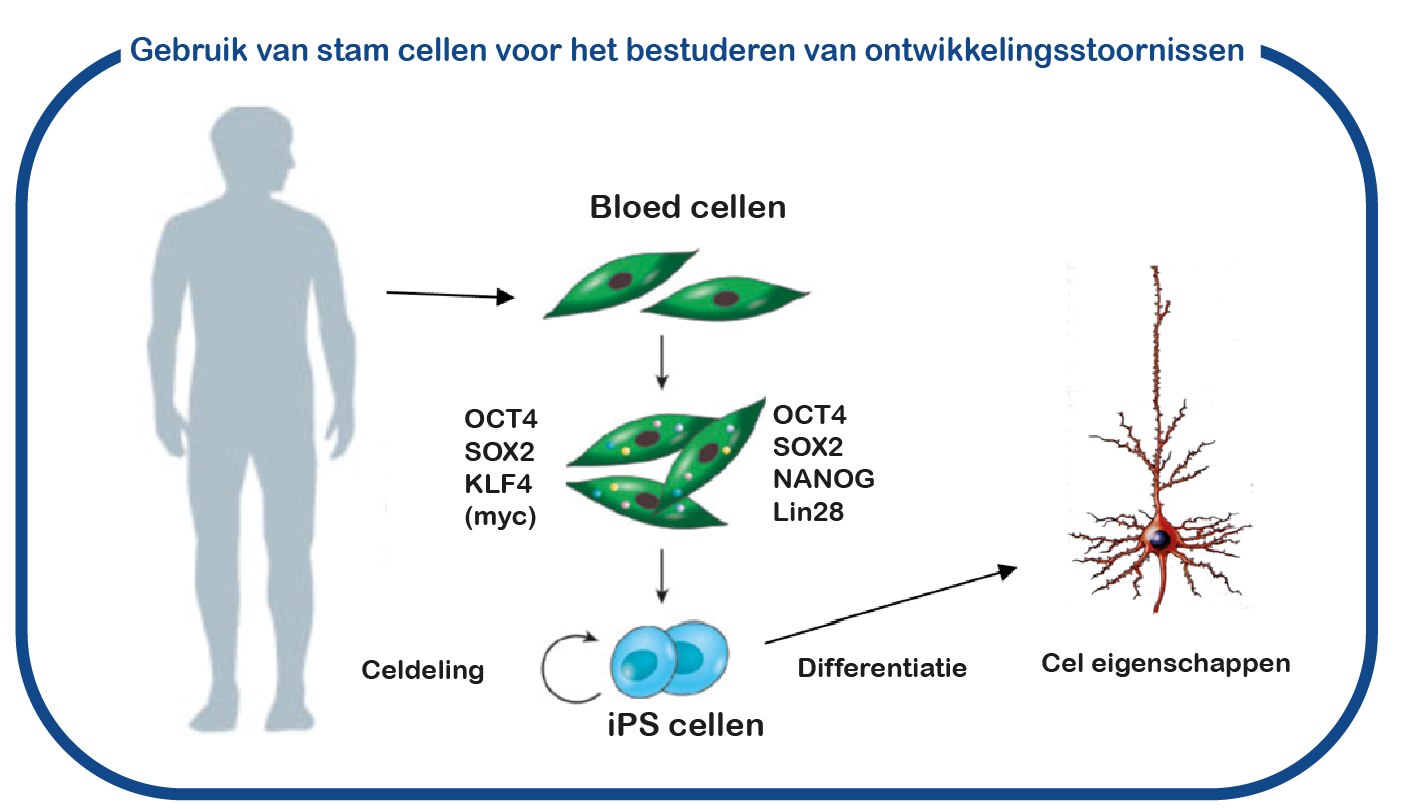
Veel van de cognitieve ontwikkelingsstoornissen die deel uitmaken van het ENCORE expertisecentrum zijn geassocieerd met autisme, en staan daarom op de ‘autisme’ genenlijst zoals hierboven getoond (bijv.UBE3A, TSC, FMR1, GRIN, de meeste RASopathieën). Er staan echter ook veel genen op deze lijst waarvoor patiënten uiterst zeldzaam zijn, met slechts 1 of enkele patiënten in Nederland. Om van deze aandoeningen te leren, hun verschillen te begrijpen en behandelmogelijkheden te onderzoeken, zijn we het expertisecentrum ‘Uniek’ (‘Uniek’) gestart. In het lab bestuderen we deze aandoeningen door gebruikmaking van geïnduceerde pluripotente stamcellen (iPS). Deze stamcellen worden gegenereerd uit bloedcellen die zijn gedoneerd door patiënten en niet-aangedane familieleden. Het grote voordeel van dergelijke iPS-cellen is dat we deze cellen kunnen differentiëren tot menselijke neuronen, waardoor we menselijke (patiënt) neuronen in een kweekschaal kunnen bestuderen. Met deze benadering hopen we te ontcijferen hoe deze mutaties de hersenen ontregelen en om nieuwe geneesmiddelen te identificeren die de hersencel functie herstelt.
Albuainain F, et.al. (2024) Confirmation and expansion of the phenotype of the TCEAL1-related neurodevelopmental disorder. Eur J Hum Genet. Pubmed
Heimer G, et al. (2020) Netrin-G2 dysfunction causes a Rett-like phenotype with areflexia. Hum Mutat 41, 476–86. Pubmed
Kumar R, et al. (2020) Expanding Clinical Presentations Due to Variations in THOC2 mRNA Nuclear Export Factor. Front Mol Neurosci. 13,1-15. Pubmed
de Vrij FM, et al. (2019) Candidate CSPG4 mutations and induced pluripotent stem cell modeling implicate oligodendrocyte progenitor cell dysfunction in familial schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 24; 757–71. Pubmed
White T, et al. (2018) Paediatric population neuroimaging and the Generation R Study: the second wave. Eur J Epidemiol. 33; 99–125. Pubmed
Bruinsma CF, et al. (2015) An essential role for UBE2A/HR6A in learning and memory and mGLUR-dependent long-term depression. Hum Mol Genet. 25; 1-8. Pubmed
Eussen, M.L. et al. (2013) The association of quality of social relations, symptom severity and intelligence with anxiety in children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism 17, 723–735. Pubmed
Marroun, El, H. et al. (2013) Prenatal Tobacco Exposure and Brain Morphology: A Prospective Study in Young Children. Neuropsychopharmacology. Pubmed
Louwerse, A. et al. (2013) Autonomic Responses to Social and Nonsocial Pictures in Adolescents With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. Pubmed
So, P. et al. (2013) Using the Child Behavior Checklist and the Teacher’s Report Form for identification of children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism 17, 595–607. Pubmed
Román, G.C. et al. (2013) Association of gestational maternal hypothyroxinemia and increased autism risk. Ann Neurol. Pubmed
Greaves-Lord, K. et al. (2013) Empirically based phenotypic profiles of children with pervasive developmental disorders: interpretation in the light of the DSM-5. J Autism Dev Disord 43, 1784–1797. Pubmed
White, T. et al. (2013) Pediatric population-based neuroimaging and the Generation R Study: the intersection of developmental neuroscience and epidemiology. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 28, 99–111. Pubmed
Jaspers, M. et al. (2013) Early childhood assessments of community pediatric professionals predict autism spectrum and attention deficit hyperactivity problems. J Abnorm Child Psychol 41, 71–80. Pubmed
Baudouin, S.J. et al. (2012) Shared synaptic pathophysiology in syndromic and nonsyndromic rodent models of autism. Science 338, 128–132. Pubmed
van der Vlugt, J.J.B. et al. (2012) Cognitive and behavioral functioning in 82 patients with trigonocephaly. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 130, 885–893. Pubmed
Hermans, H. et al. (2012) Feasibility, reliability and validity of the Dutch translation of the Anxiety, Depression And Mood Scale in older adults with intellectual disabilities. Res Dev Disabil 33, 315–323. Pubmed
Vuijk, R. et al. (2012) Personality traits in adults with autism spectrum disorders measured by means of the Temperament and Character Inventory. Tijdschr Psychiatr 54, 699–707. Pubmed
Nijmeijer, J.S. et al. (2010) Perinatal risk factors interacting with catechol O-methyltransferase and the serotonin transporter gene predict ASD symptoms in children with ADHD. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51, 1242–1250. Pubmed
Tiemeier, H. et al. (2010) Cerebellum development during childhood and adolescence: a longitudinal morphometric MRI study. Neuroimage 49, 63–70. Pubmed
de Bruin, E.I. et al. (2009) Autistic features in girls from a psychiatric sample are strongly associated with a low 2D:4D ratio. Autism 13, 511–521. Pubmed
Herba, C.M. et al. (2008) Face and emotion recognition in MCDD versus PDD-NOS. J Autism Dev Disord 38, 706–718. Pubmed
de Bruin, E.I. et al. (2007) Multiple complex developmental disorder delineated from PDD-NOS. J Autism Dev Disord 37, 1181–1191. Pubmed
de Bruin, E.I. et al. (2007) High rates of psychiatric co-morbidity in PDD-NOS. J Autism Dev Disord 37, 877–886. Pubmed
de Bruin, E.I. et al. (2006) Differences in finger length ratio between males with autism, pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified, ADHD, and anxiety disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol 48, 962–965. Pubmed
de Bruin, E.I. et al. (2006) WISC-R subtest but no overall VIQ-PIQ difference in Dutch children with PDD-NOS. J Abnorm Child Psychol 34, 263–271. Pubmed
Dekker, M.C. et al. (2002) Assessing emotional and behavioral problems in children with intellectual disability: revisiting the factor structure of the developmental behavior checklist. J Autism Dev Disord 32, 601–610. Pubmed
van der Geest, J.N. et al. (2002) Gaze behavior of children with pervasive developmental disorder toward human faces: a fixation time study. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 43, 669–678. Pubmed
van der Geest, J.N. et al. (2002) Looking at images with human figures: comparison between autistic and normal children. J Autism Dev Disord 32, 69–75. Pubmed
